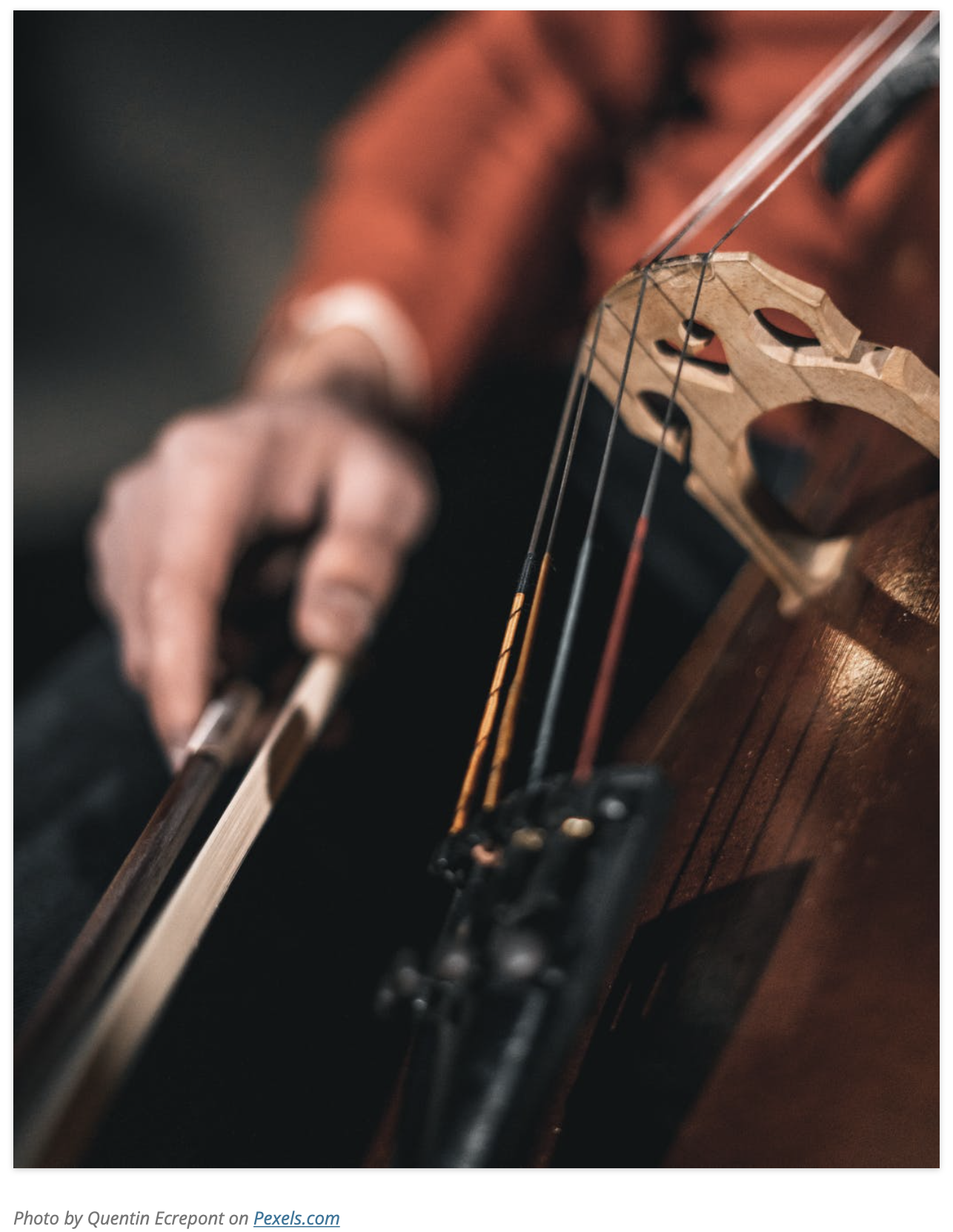
When you’re playing music (or engaging in any activity, for that matter), all your habits of unnecessary tension have one thing in common: they tend to diminish your stature rather than expand it.
Essentially, you become smaller. You compress yourself. You lessen the space within.
It is sometimes difficult to discern unnecessary tension because you are so habituated to how it feels. Often you don’t feel the “tension” until it morphs into pain. And sometimes, even the pain you accept as the price to pay for playing your instrument (though in reality, this does not have to be the case!)
So tension can be an almost abstract idea, a subjective matter. That’s why I like to include the idea of thinking about the space within ourselves as we play.
As I get further along teaching the Alexander Technique, I find myself bringing more of my student’s attention to their space. My aim is to tie their perception of tension into their awareness of their own space, helping them to think more expansively.
This tends to get them to stop trying too hard to feel (and judge) what may or may not be tension. It brings their attention more outward, making it more inclusive of themselves and of their other senses. Always good results when this happens.
So as you practice, take stock of your space. Where are you closing yourself off as you play? Notice how closing yourself off changes the ease and balance of what you do.
Here are a few things you can do to help you perceive and maintain your internal space, and reduce lots of unnecessary tension:
- Notice yourself and your instrument-Are you collapsing and compressing down into your instrument? If so, see if you can think lightly up and away from it instead.
- Notice your head and neck-Let your head balance lightly upon your spine, releasing it in an upward direction (Don’t tighten and compress your neck.) You can even think about allowing more space in your mouth and jaw. Even around your eyes.
- Notice your shoulders, hands and arms-Are you pulling your shoulders back? Or collapsing them forward as you close the space of in your chest? Are your arms plastered against your rib cage closing off the space between your arms and torso? Are your hands, wrists and fingers compressed? Allow yourself to release into length and width.
- Notice your back and hips– Notice if you tend to either tuck your pelvis, thrust it forward, and/or arch your back when you play. Let your pelvis release away from the crown of your head, creating more length in your entire torso.
- Notice your knees-Are you locking your knees by pulling them backwards? How does this affect the space, not only in your legs, but in your lower back and hips?
- Notice your feet-Are your feet “holding on the the floor” in tension? Do you feel most of your weight in the balls of your feet? Let your weight drop down to the ground through your ankle bones and slightly into your heels. Notice how you gain more space in your feet (and the rest of your body!) when you do this.
- Notice your breathing-Are you holding on to your rib cage as you breathe? Are you stiffening your neck? Healthful, efficient breathing involves movement of your entire torso, flowing from gentle contraction to expansion in three dimensions. Allow space in your entire torso to let this happen.
In the Alexander Technique we use something called the primary directions to help us to think about releasing into expansion. The directions are simply a description of how our bodies naturally expand into our full space. Thinking about them can help you with some of the habits of compression I’ve listed above. Here they are:
I allow my neck to be free so that my head can release forward and upward on top of my spine
So that my entire torso can lengthen and widen,
So that my knees can release forward from my hip joints, and one knee can release away from the other,
So that my heals can release into the ground
And that’s it. All you have to to do is think the directions and you’ll start to find your space again. Get to really know the directions and use them often. By doing so you’ll keep much of that unnecessary tension in check.